Explore the Serapeum of Alexandria: The Lost Temple of Serapis

I. The History and Importance of the Serapeum of Alexandria
The Serapeum of Alexandria is a fascinating ancient temple with significant religious and cultural importance in Alexandria, Egypt. Built during the reign of Ptolemy III in the 3rd century BC, it was dedicated to the god Serapis, a syncretic deity combining aspects of Greek and Egyptian gods. The temple symbolised cultural fusion and a centre for knowledge and scholarship.
The Serapeum was one of the largest and most magnificent temples in the ancient world, known for its grand architecture and intricate decorations. It housed a vast library known as the Serapeum Library, renowned for its collection of scrolls and manuscripts. Scholars from all over the world would visit the temple to study and exchange knowledge.
Unfortunately, much of the temple was destroyed during the Christianization of Alexandria in the late 4th century AD. The once glorious Serapeum was lost to history, and its ruins were buried beneath the modern city. However, recent archaeological excavations have uncovered fragments of the temple, providing valuable insights into the ancient past.
You can visit its Wikipedia page to learn more about the rich history and significance of the Serapeum of Alexandria.

II. The Origins of the Serapeum
The Serapeum of Alexandria, also known as the Temple of Serapis, was a magnificent and sacred structure in Alexandria, Egypt. It was built during the reign of Ptolemy III Euergetes in the 3rd century BC and dedicated to the Egyptian deity Serapis, a syncretic combination of the Egyptian god Osiris and the Greek god Zeus or Hades. The temple was designed by the architect Deinocrates of Rhodes and was considered one of Alexandria's most significant religious and cultural centres.
The Construction and Purpose of the Temple
The Serapeum was an architectural masterpiece, incorporating elements of both Egyptian and Greek styles. It featured a massive collonaded courtyard, a main hall with a central shrine dedicated to Serapis, and various smaller chambers and rooms. The temple's exterior was adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures, showcasing the expertise of ancient craftsmen.
The purpose of the Serapeum was to serve as a place of worship for the cult of Serapis, which was introduced during the Hellenistic period. Serapis was believed to be a powerful deity associated with fertility, the afterlife, and healing. The temple attracted devotees from all over the Mediterranean region who sought blessings, divine guidance, and protection from Serapis.
The Serapeum also significantly influenced Alexandria's intellectual and cultural landscape. It housed a vast library known as the Serapeum Library, which contained a vast collection of scrolls and manuscripts that rivalled the famous Library of Alexandria. Scholars, philosophers, and intellectuals would gather at the temple to exchange ideas, engage in philosophical discussions, and pursue knowledge.
Today, sadly, the Serapeum no longer stands. Over the centuries, the temple faced numerous challenges, including earthquakes, religious conflicts, and the decline of the ancient city of Alexandria. The remaining ruins of the Serapeum can still be seen, giving us a glimpse into its former glory.
To learn more about the Serapeum of Alexandria and its significance in ancient history, visit here.

III. Serapis: The God of the Serapeum
The Cult of Serapis and its Significance in Ancient Egypt
The Serapeum of Alexandria, also known as the Lost Temple of Serapis, was dedicated to the worship of the god Serapis. Serapis was a Hellenistic deity who emerged during the Ptolemaic dynasty in Ancient Egypt. This section will explore the cult of Serapis and its significance in Ancient Egypt.
The Cult of Serapis:
- Serapis was a composite deity, combining attributes of the Egyptian god Osiris and the Greek god Zeus.
- The cult of Serapis was established by Ptolemy I after he unified Egypt under Greek rule.
- Serapis was worshipped by both Greek and Egyptian communities, serving as a symbol of cultural blending and religious tolerance.
- The cult of Serapis gained popularity throughout the Hellenistic world and continued to be venerated even after the decline of the Ptolemaic dynasty.
Significance in Ancient Egypt:
- Serapis represented the idea of syncretism, the merging of different religious traditions.
- The cult of Serapis played a crucial role in promoting a sense of unity and harmony among the diverse population of Alexandria.
- The Serapeum of Alexandria, with its grand architectural features and sacred rituals, became a centre for religious pilgrimage and cultural exchange.
- The worship of Serapis also extended beyond Egypt, influencing other Mediterranean cultures and establishing Serapeums in various cities.
To learn more about the fascinating cult of Serapis and its significance in Ancient Egypt, you can visit this Wikipedia page.

IV. The Architecture of the Serapeum
The Design and Layout of the Temple Complex
The Serapeum of Alexandria was a magnificent temple complex dedicated to the worship of Serapis, a Greco-Egyptian god. The architecture of the Serapeum showcased the grandeur and splendour of ancient Egyptian and Greek influences. Here are some key features of the temple complex:
1. Three-Tiered Design: The Serapeum was built on three levels, each representing a significant aspect of the temple complex. The lowest level consisted of the main temple and the sanctuary of Serapis. The middle level housed various chambers and shrines, while the upper level was adorned with beautiful gardens and statues.
2. Corinthian Columns: The entrance of the Serapeum was marked by a grand colonnade of Corinthian columns. These columns were known for their intricate detail and elegant design, adding a sense of grandeur to the temple complex.
3. Statues and Obelisks: The Serapeum was adorned with numerous statues and obelisks, each representing different deities and significant figures in Egyptian and Greek mythology. These statues and obelisks were intricately carved and served as a testament to the artistic skill and craftsmanship of the time.
4. Subterranean Complex: Beneath the main temple, a vast network of tunnels and chambers served as sacred burial grounds for the sacred Apis bulls. These subterranean chambers were believed to house the remains of the revered bulls and were considered highly sacred.
5. Axial Alignment: The Serapeum was constructed with precision and a strong sense of axial alignment. The main temple and the various chambers were aligned in a specific order, highlighting the importance of symmetry and balance in the design of the temple complex.
The Serapeum of Alexandria was a remarkable feat of architecture, blending the influences of various cultures and showcasing the rich history of ancient Egypt and Greece. Although the temple complex is no longer standing, the remnants and historical records provide a glimpse into the grandeur and significance of this once-magnificent site.
Take a closer look at the awe-inspiring architecture and design of the Serapeum of Alexandria by visiting its Wikipedia page.

V. The Serapeum and Ancient Alexandria
The Relationship Between the Temple and the City
The Serapeum of Alexandria was a significant religious site and played a crucial role in the ancient city of Alexandria. Here are some key insights into the relationship between the temple and the city:
1. Cultural and Religious Center: The Serapeum was considered the heart of cultural and religious life in ancient Alexandria. It was dedicated to the Egyptian god Serapis, who was seen as a fusion of Greek and Egyptian deities. As a result, the temple became a symbol of the blending of Greek and Egyptian cultures in Alexandria.
2. Seat of Knowledge: The Serapeum housed a vast library that rivalled the famous Library of Alexandria. It was a centre of learning and scholarship, attracting scholars and philosophers from around the ancient world. The library within the temple was home to countless scrolls and manuscripts, making it a hub of intellectual activity.
3. Political Significance: The temple played a significant role in the political landscape of Alexandria. It symbolized the power and authority of the Ptolemaic dynasty, the ruling family of ancient Egypt. It was also where important ceremonies and rituals began, solidifying the rulers' connection to the divine.
4. Architectural Marvel: The Serapeum was an architectural masterpiece showcasing the skills and craftsmanship of ancient Alexandrians. The temple featured a grand entrance, massive columns, intricate carvings, and statues depicting various deities. Its grandeur and beauty added to its significance within the city.
5. Decline and Destruction: Unfortunately, the Serapeum declined in the 3rd century AD and was eventually destroyed during the conflict between paganism and Christianity. The temple was seen as a symbol of paganism and was systematically targeted by early Christians.
Despite its eventual destruction, the Serapeum remains an intriguing and significant site, representing ancient Alexandria's rich history and cultural exchange. To learn more about the temple and its importance in ancient Alexandria, you can visit this Wikipedia page.
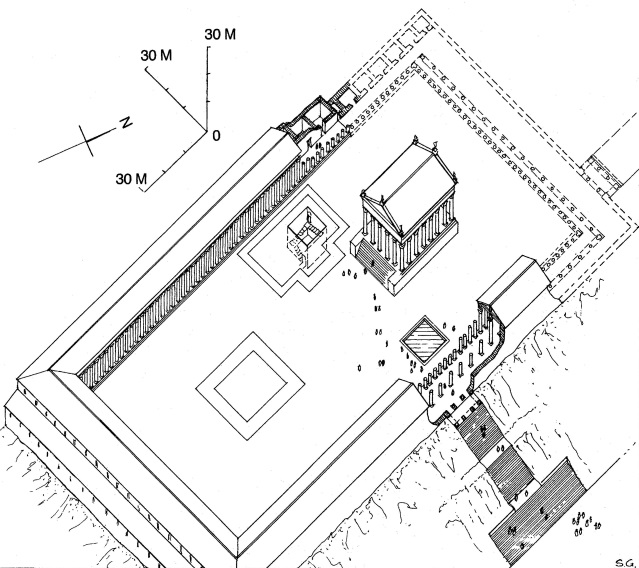
VI. Rediscovering the Serapeum
Archaeological Excavations and Discoveries at the Site
The Serapeum of Alexandria, also known as the Lost Temple of Serapis, was a magnificent ancient temple dedicated to the Greco-Egyptian god Serapis. The temple was built during the reign of Ptolemy III in the 3rd century BC and served as a centre of worship and learning in ancient Alexandria. However, the temple was lost and buried beneath the city after centuries of neglect and destruction.
In recent years, archaeological excavations have sought to rediscover and uncover the mysteries of the Serapeum. These excavations have revealed fascinating insights into the history and architecture of this ancient religious site. Here are some of the key discoveries made at the site:
-
The Foundation: Excavations have uncovered the massive foundation of the Serapeum, revealing the temple's grand scale and impressive architecture. The foundation measures approximately 120 meters long and 40 meters wide, showcasing the monumental nature of the temple.
-
Statues and Reliefs: Various statues and reliefs depicting gods, goddesses, and other mythical figures have been discovered at the site. These artworks provide valuable glimpses into the religious beliefs and practices of the ancient Egyptians.
-
Crypts and Chambers: Deep within the foundations of the Serapeum, archaeologists have uncovered a network of crypts and chambers. These underground spaces likely served as sacred burial sites or places of ritualistic practices.
-
Library of the Serapeum: The Serapeum was known for its vast library, housing a collection of rare manuscripts and scrolls. While much of the library's contents have been lost to history, the discovery of fragments and remnants point to the intellectual and scholarly significance of the temple.
-
Cultural Exchange: The Serapeum of Alexandria was a hub of cultural exchange, attracting scholars, philosophers, and religious pilgrims from various parts of the ancient world. The site's archaeological findings highlight the temple's cosmopolitan nature and its role in facilitating intellectual discourse.
The ongoing excavations at the Serapeum of Alexandria provide a fascinating glimpse into the rich history of ancient Alexandria and its prominent religious site. These discoveries not only shed light on the architectural and artistic achievements of the ancient Egyptians but also offer insights into the time's social, cultural, and religious practices. To learn more about the Serapeum and its significance, you can visit this Wikipedia page.

VII. The Destruction of the Serapeum
The Decline and Fall of the Temple
As the centuries passed, the once-mighty Serapeum of Alexandria began to see a decline in its significance and popularity. The rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire played a significant role in the temple's eventual downfall. With the spread of Christianity, traditional pagan worship came under increasing scrutiny and persecution.
In the 4th century AD, Emperor Theodosius I issued a series of decrees that sought to suppress pagan worship and promote Christianity as the empire's official religion. The Serapeum in Alexandria was targeted, as it represented one of the last bastions of ancient Egyptian religion.
The destruction of the Serapeum took place in 391 AD, following an edict issued by Theodosius I. Christian mobs, encouraged by the edict, attacked the temple and ravaged its grand halls and magnificent statues. The library housed within the Serapeum is said to have also been destroyed during this time.
The fall of the Serapeum marked the end of an era. The once-great temple, dedicated to the god Serapis, was reduced to ruins, and its name faded from memory. Today, all that remains are fragments and pieces of what was once a majestic centre of worship and learning.
To learn more about the fascinating history of the Serapeum of Alexandria, you can visit this Wikipedia page that provides detailed information about its architecture, significance, and ultimate destruction.

VIII. The Legacy of the Serapeum
The Influence of the Temple on Art, Religion, and Culture
The Serapeum of Alexandria, also known as the Lost Temple of Serapis, left a lasting impact on ancient Alexandria's art, religion, and culture. This magnificent temple was dedicated to Serapis, the Greek-Egyptian god, and was considered one of the most important religious centres in the city.
1. Art and Architecture: The Serapeum showcased the architectural prowess of ancient Alexandria. Its grand columns, intricate carvings, and impressive statues were a testament to the skill and creativity of the craftsmen of that era. The temple's design influenced subsequent architectural styles, and its grandeur set a new standard for religious structures.
2. Religious Syncretism: The Serapeum played a crucial role in the syncretism of Greek and Egyptian religious beliefs. Serapis, a combination of Greek and Egyptian deities, became a central figure in the religious practices of ancient Alexandria. This blending of religious traditions helped foster cultural integration and mutual understanding among the city's diverse population.
3. Center of Knowledge: The Serapeum was not only a place of worship but also a centre of knowledge. Its library housed a vast collection of scrolls and manuscripts, rivalling the famous Library of Alexandria. Scholars, philosophers, and intellectuals frequented the temple, engaging in academic pursuits and intellectual debates.
4. Cultural Exchange: The Serapeum's prominence also attracted travellers, traders, and visitors from different regions. This cultural exchange led to the cross-pollination of ideas, beliefs, and artistic styles, enriching the cultural fabric of Alexandria.
The Serapeum's influence continued long after the temple's destruction. Today, remnants of its grandeur can still be seen in the archaeological sites of Alexandria, providing glimpses into the city's vibrant past.
For further information on the Serapeum and its historical significance, you can visit this Wikipedia page.

IX. The Serapeum Today
Visiting and Exploring the Ruins
Today, the Serapeum of Alexandria is a haunting reminder of the city's ancient past. Although much of the temple has been lost to time and archaeological excavations, there are still fascinating remnants to explore. Here's what you can expect when visiting the ruins of the Serapeum:
1. The Semicircular Theater: One of the most well-preserved sections of the Serapeum is the semicircular theatre, which once served as a gathering place for religious ceremonies and cultural performances.
2. The Serapeum Library: The Serapeum was renowned for its impressive library, which housed countless scrolls and texts. While most of the library's contents have been lost, you can still see the remnants of the structure, including its architectural elements and the niches where scrolls were stored.
3. The Hypostyle Hall: The Hypostyle Hall was a grand hall with rows of towering columns. Only a few columns remain standing today, but they offer a glimpse into the temple's former grandeur.
4. The Underground Crypts: Beneath the temple complex lie a series of underground crypts. These crypts were used for religious rituals and as a burial place for sacred animals. Exploring these underground chambers can be a fascinating experience.
Visiting the Serapeum is like stepping back in time, allowing you to immerse yourself in ancient Alexandria's rich history and culture. While the temple may no longer witness religious ceremonies, its ruins provide a window into the past and a chance to marvel at the architectural brilliance of the ancient Egyptians.
If you're planning a trip to Alexandria, add the Serapeum to your itinerary. It's a must-visit destination for history buffs, archaeology enthusiasts, and anyone interested in exploring the mysteries of the ancient world.
To learn more about the history and significance of the Serapeum of Alexandria, visit the Serapeum of Alexandria Wikipedia page.

X. Mysteries and Legends of the Serapeum
The Serapeum of Alexandria, also known as the Lost Temple of Serapis, has fascinated historians, archaeologists, and curious minds for centuries. This ancient temple, dedicated to the Egyptian god Serapis, was once a worship centre and held great significance in the ancient world. Despite its historical prominence, much about the Serapeum remains shrouded in mystery. Here are some unanswered questions and intriguing tales surrounding this enigmatic site:
Unanswered Questions
-
What happened to the famed Serapeum Library? The Serapeum was known to house a vast collection of ancient texts, rivalling the famous Library of Alexandria. However, the fate of this library and its priceless manuscripts remains unknown.
-
How was the Serapeum destroyed? The temple suffered numerous attacks and was eventually destroyed, but the exact circumstances are still debated among scholars. Some attribute its downfall to religious conflicts, while others suggest natural disasters or political upheaval.
-
Is the Serapeum truly lost? While the temple may be in ruins, many believe there are still undiscovered chambers and hidden treasures within its walls. Archaeologists continue to search for clues that may lead to uncovering these secrets.
Intriguing Tales
-
The Curse of the Serapeum: Legend states that anyone who desecrates the temple or removes its artefacts will be cursed. Several tales tell of misfortunes befalling those who have dared to disturb the sacred site, adding to the allure and mystery surrounding the Serapeum.
-
The Serapeum's Hidden Treasures: Rumors persist of untold riches buried beneath the temple grounds. Some believe that looters may have already uncovered these treasures, while others hold out hope that hidden chambers are still waiting to be explored.
The Serapeum of Alexandria remains a captivating enigma, its secrets waiting to be unravelled by future discoveries and research. As archaeologists continue to delve into this ancient site, we may one day uncover the truth behind the mysteries and legends of the Serapeum.
